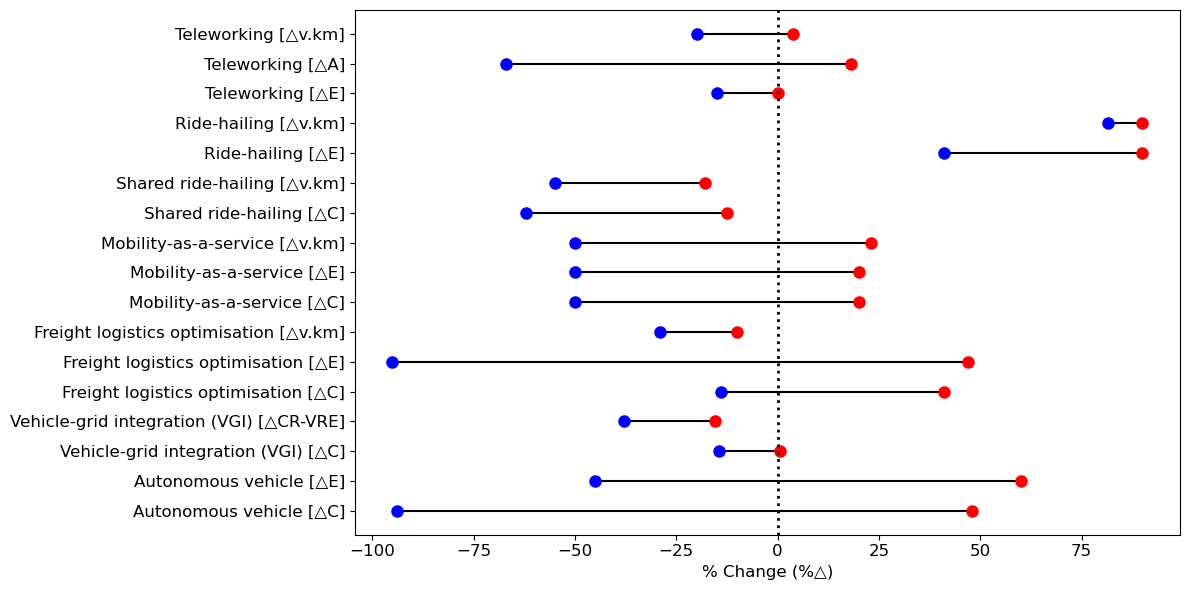
CircEUlar members from the University of Oxford team recently published their insights on the impact of digitalisation in the Oxford Energy Forum, a quarterly journal dedicated to energy issues and policy debates. In the article featured in the issue on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Its Implications for the Electricity System, Charlie Wilson and Yee Van Fan argue that the indirect impacts of AI on climate may outweigh concerns about the energy needed to train and run AI models. This perspective aligns with one of the motivations of the CircEUlar project, which seeks to assess the broader role of digitalisation.
The indirect impacts of digitalisation are highly uncertain, as also recently highlighted in the latest report by the International Energy Agency. These impacts are expected to play a larger role in the net-zero transition, both positively and negatively, than the direct footprint of digital infrastructure (e.g., data centres), which is more relevant to local energy planning.
In the article, Charlie and Yee Van describe digitalisation or AI applications as a double-edged sword, with their ultimate impact depending on the specific application area and deployment context. While some digital tools offer unambiguous benefits for circularity, energy efficiency, or greenhouse gas reduction, others are unambiguous detrimental. Most applications, however, fall somewhere in between, with outcomes dependent on factors such as rebound effects, the ability to manage them, and patterns of adoption or diffusion.
Although there is emerging evidence on the indirect impacts of digitalisation, as summarised in Wilson et al. (2024), the implications of the identified case specific results for the future and on a global scale remain underexplored and not well understood. At this stage, assessments at country, region or global level are largely exploratory and highlight the need for more systematic and transparent methodologies to evaluate the role or impact of digitalisation on the mitigation pathway.
By the end of the CircEUlar project, a more structured and detailed mapping of enabling conditions and the estimated impact of digitalisation is expected. Efforts in this direction have been previously reported, including analysis of two digital applications in the bulk materials and buildings sector.
By Charlie Wilson and Yee Van Fan – UOXF
